OS.Walk and Fnmatch in Python Python Array

Python 13 Directories and OS Walk YouTube
Python has a cool built-in function in the OS module that is called os.walk () . OS.walk () generate the file names in a directory tree by walking the tree either top-down or bottom-up. For each directory in the tree rooted at directory top (including top itself), it yields a 3-tuple (dirpath, dirnames, filenames).

OS.Walk and Fnmatch in Python Python Array
Example. The following example shows the usage of walk () method. # !/usr/bin/python import os for root, dirs, files in os.walk(".", topdown=False): for name in files: print(os.path.join(root, name)) for name in dirs: print(os.path.join(root, name)) Let us compile and run the above program, this will scan all the directories and subdirectories.

os.walk Traversing a directory tree bottomup using Python Stack Overflow
The first argument to your callback function is the last argument of the os.path.walk function. Its most obvious use is to allow you to keep state between the successive calls to the helper function (in your case, myvisit). os.path.walk is a deprecated function. You really should use os.walk, which has no need for either a callback function or helper arguments (like a in your example).
Python os.walk() A Simple Illustrated Guide Be on the Right Side of Change
OS.walk () generate the file names in a directory tree by walking the tree either top-down or bottom-up. For each directory in the tree rooted at directory top (including top itself), it yields a 3-tuple (dirpath, dirnames, filenames). root : Prints out directories only from what you specified.
os.walk()の返す値をごにょごにょするshift_path()って関数作った Humanity
Step 4: Use the isfile () Function. Every iteration of the loop must have the os.path.isfile ('path') function to verify whether the current path is a file or a directory. If the function finds that it is a file, it returns True, and the file is added to the list. Else the function returns False.

python os.walk example
The walk function of the os module takes one required argument and several optional ones. The address of a directory must be passed as a required argument. The walk () function returns a generator object from which to get tuples. Each tuple "describes" one subdirectory from the directory tree passed to the function. Each tuple has three items.

Python Os Walk Recursive Examples Decoding Devops Decodingdevops Riset
os.walk() is a part of Python's os built-in module.The os module consists of operating system interfaces.It gives us a portable way of using os-dependent functionality in our Python code. os.walk allows us to generate file names in a directory tree by "walking the tree" - (we can get folders, subfolders, and files at every level).A tuple of three elements is returned for each directory in the.
Python os.walk() A Simple Illustrated Guide Be on the Right Side of Change
The Python os walk() method generates the file names in the directory tree by walking the tree either top-bottom or bottom-top. We now have a youtube channel.. Example. The following below is a simple example - # !/usr/bin/python import os for root, dirs, files in os. walk.
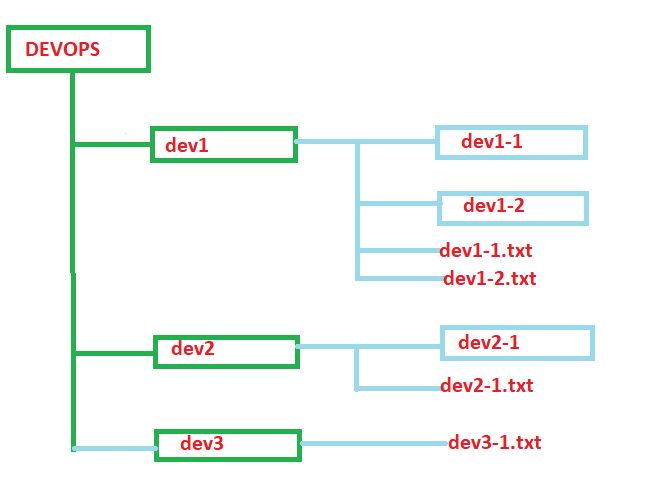
Python OS Walk Recursive Examples /Decoding/Devops DecodingDevOps
In simple words os.walk () will generate tuple of path,folders,files present in given path and will keep on traversing the subfolders. First note that os.walk () items, the root directory, a list of directories () immediately below the current root and a list of files found in those directories.

Python Os.Walk? The 21 Detailed Answer
Python os.walk() method is used to generate the file names in the file index tree by walking either top-down or bottom-up.. This function will help you traverse a directory. Each directory in the tree rooted at the top of the directory generates a 3-tuple: dirpath, dirnames, and filenames. Syntax

Overview In an earlier post "OS.walk in Python", I described how to use os.walk and showed some
The os.walk () method generates the file and directory names in a directory tree by walking the tree using top-down or bottom-up approach. Each directory in the tree is rooted to the top directory. It yields a tuple that contains directory path, directories name and file name. The os.walk () method use os.scandir () method for produce listing.

python os.walkos.system in python Python Tutorial 12 Python Tutorial for Beginners YouTube
Example Codes: Use the os.walk () Method With the followlinks Parameter. In this example, we will scan the current directory for files and folders and follow any symbolic links. import os for parent, subdirs, files in os.walk(".", followlinks=True): for filename in files: print(os.path.join(parent, filename)) for subdir in subdirs: print(os.

python os.walk example
The os.walk example returns a generator object that contains a tuple for each directory it visits. Exploring the Tuple Returned by the os.walk Example . The tuple returned by the os.walk example contains three values. The first value is the path to the directory being visited. The second value is a list of the subdirectories in the directory.

OS.Walk and Fnmatch in Python Python, Improve yourself, Tutorial
From docs.python.org:. os.walk(top[, topdown=True[, onerror=None[, followlinks=False]]]) When topdown is True, the caller can modify the dirnames list in-place. this can be used to prune the search.

os.walk() in Python
#os #walk #directories #files #python #tutorial #explain #how #use #subThis is a wonderful and informative class dedicated to the os.walk() method. In this.
SampleData · master · ILS Research / oswalkeuqgisplugin · GitLab
Python os.walk () Example-3 with Recursive: import os x=r'C:\Users\enaknar\Desktop\pycharm\devops' for r,d,f in os.walk (x): for i in d: print (i) here it will print all the directories and sub directories names, but not with complete path from root. so to traverse a directory tree we can use python os.walk () method.